We must accept the fact that the faster we go, the further it will take us to stop. Several things must be considered to determine the stopping distance.
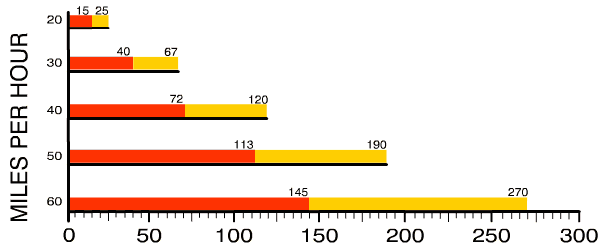 | |
The above graph indicates the reaction (red) and braking (gold) distance for the total braking distance at various speeds. |
Your mental and physical condition is very important.
Of course, age, use of drugs, and physical fatigue will all affect your ability to react to a potential hazard, sometimes called perception and reaction time. Reaction time in daily driving can be as high as 1.5 seconds with various driving distractions.
The vehicle is another important factor to be considered in the stopping distance. Vehicles must have brakes that meet certain standards. We have even developed alternative braking systems such as Anti-locking Braking Systems (ABS).
The road and weather conditions all must be considered. As we discussed in another section of the manual, friction is the most important factor in stopping a vehicle.
When you are forced to stop, three things must happen. You must perceive the hazard or warning; react; and use your brakes to stop.
The length of time you take to identify, predict, and decide to slow for a hazard is called your perception time. You cannot consistently estimate your perception time because your ability to perceive will change from time to time. By scanning and maintaining the proper spacing method that we discussed earlier, you allow yourself more reaction time.
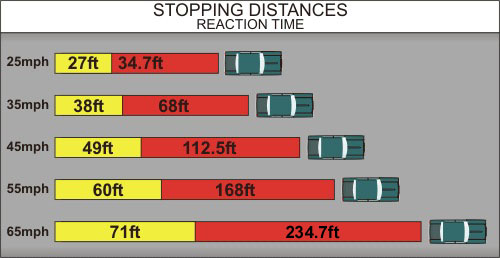
Once you know a hazard will be a problem, the length of time you take to execute your actions is your reaction time. An average driver's reaction time is ¾ of a second, in clinical laboratory settings. If you are impaired due to alcohol, drugs or fatigue, your reaction time will increase; thus the time to stop and distance that your car travels will also increase.
The distance your vehicle travels from the time you apply the brakes until your vehicle stops is called braking distance. These distances will change depending on your ability at the time, your vehicle conditions, and the conditions of the road. Estimating stopping distance can be hard so it is always better to utilize the two second rule. This rule enables you to project your approximate stopping distance under ideal conditions at any speed.
Don't forget, the higher the speed, the longer the braking distance. At higher speeds, you will have a harder time controlling your vehicle. A vehicle with worn tires or bad brakes needs a longer distance to stop. If the brakes on one side of your car are worn or out of adjustment, your vehicle will pull to one side in a stop. If you panic and slam on your brakes you might lose control of your car in an emergency situation. Remember wet road surfaces will reduce traction on the road and increase your braking distance.
No comments:
Post a Comment